The Evolution and Impact of Data Products [A Deep Dive]
![The Evolution and Impact of Data Products [A Deep Dive]](/content/images/size/w960/2023/11/Group-1--3-.png)
Welcome, data people, to another riveting journey through the vast realm of Data and Software Engineering! Today, we're delving deep into the fascinating world of "Data Products," where the currency isn't dollars or euros, but the invaluable bits and bytes that fuel our digital existence.
Buckle up, it's gonna be a long one! I had some time off work lately which allowed me to write more than usual 😁.
In this article, we'll unravel most of the mysteries surrounding Data Products, those ingenious innovations where the main offering isn't a tangible service like hailing a cab or connecting with friends. Instead, it's the data itself that takes center stage, steering the wheel of technological progress.
Now, you might wonder, "Why should I trust this data maestro to guide me through the intricacies of data-driven wonders?" Well, dear reader, with a track record of navigating the ever-evolving landscapes of Data and Software Engineering, coupled with hands-on experiences and a knack for decoding complex concepts into palatable wisdom, you're in expert hands.
But let's not linger on the introductions too long—there's a trove of knowledge waiting to be uncovered! Buckle up as we journey through the dimensions of Data Products, exploring their significance, dissecting real-world examples, and peering into the future where data isn't just a commodity; it's the heartbeat of innovation. Ready? Let's dive in!
Understanding the Landscape
In the vast and ever-evolving landscape of technology, the distinction between traditional services and the emerging realm of Data Products is more crucial than ever. Imagine calling an Uber to whisk you away or posting updates on Facebook – these are services we're all familiar with. Now, shift your perspective to something like Spotify's Discover Weekly or the intuitive magic of Google Maps. What sets these apart? They belong to a category where the primary offering isn't an immediate service but an ongoing, evolving product fueled by data – welcome to the world of Data Products.
Differentiating Data Products from Services
Let's dissect this distinction. Services, like Uber or Facebook, provide immediate solutions to specific needs – a ride or a platform for social interaction. On the other hand, Data Products, such as Spotify's playlist recommendations or Google Maps' dynamic route suggestions, go beyond fulfilling a single transactional need.
They continuously refine and customize their offerings based on the data they collect. It's not just about the ride or the map; it's about the ongoing, personalized experience crafted through a constant loop of data analysis and user feedback.
Real-world Examples
To solidify this concept, let's delve into some real-world examples that showcase the brilliance of Data Products. Consider Spotify's Discover Weekly – that magically curated playlist tailored precisely to your musical taste. How does it know you better than your closest friends? It's not clairvoyance; it's data analytics. Spotify analyzes your listening history, compares it to others with similar tastes, and creates a personalized playlist that evolves over time. It's not just a service giving you music; it's a musical companion learning and growing with you.
Now, shift gears to Google Maps. It's not merely a static map; it's a dynamic guide adapting to your real-time needs. Whether it's suggesting the fastest route based on current traffic conditions or recommending nearby places based on your preferences, Google Maps transforms raw geographical data into a personalized service. The more you use it, the better it understands your habits, creating an ever-improving, personalized navigation experience.
These real-world instances exemplify the transformative power of Data Products. They aren't confined to providing a service; they're crafting an ongoing, evolving experience tailored to the individual user.
The Power of Data Monetization
In the expansive universe of Data Products, where information reigns supreme, an often-overlooked aspect makes the data-driven wheels turn – the power of monetization. It's not just about insights and personalized experiences; it's about converting that data into a currency that fuels innovation, growth, and, yes, the bottom line.
How Data Products Drive Revenue
Data Products are not just about providing insights; they are revenue-generating engines. Imagine your favorite social media platform – every click, every like, every share contributes to a treasure trove of data. This data, when strategically harnessed, can be transformed into revenue streams. From subscription models to targeted advertising, organizations are finding innovative ways to capitalize on the wealth of information their Data Products generate.
Like the personalized recommendations on your favorite e-commerce platform. Ever wondered how they seem to know exactly what you want? It's not magic; it's the intelligent analysis of your browsing and purchasing history. These platforms leverage this information to tailor recommendations, increasing the likelihood of a purchase. In essence, Data Products become not just tools for enhancing user experience but also strategic assets for driving sales and revenue.
Success Stories of Profitable Data Products
To truly appreciate the impact of data monetization, let's delve into success stories where organizations have mastered the art of turning data into dollars. Take Amazon, for instance – a retail giant that doesn't just sell products but excels in recommending them. Their recommendation engine analyzes user behavior, understands preferences, and suggests products tailored to individual tastes. This enhances user satisfaction and significantly contributes to Amazon's revenue through increased sales.
Similarly, consider the streaming giant, Netflix. Their recommendation algorithm, powered by machine learning, ensures you're always presented with content that aligns with your viewing habits. This keeps subscribers engaged, leading to increased retention rates and, ultimately, more revenue for Netflix. These success stories showcase how Data Products can be not just functional but financially lucrative components of a business strategy.
Pitfalls to Avoid in Monetizing Data
However, the path to data monetization has its challenges and pitfalls. As organizations navigate the data landscape, ethical and practical considerations come to the forefront. Privacy concerns, data security, and regulatory compliance become crucial factors that can make or break the success of Data Products.
Consider the delicate balance organizations must strike between leveraging user data for personalized experiences and respecting user privacy. Overstepping this line can lead to backlash, eroding user trust and potentially causing financial and reputational damage. Additionally, as data regulations evolve, staying compliant becomes a perpetual challenge for organizations seeking to monetize their data.
Building Blocks of Data Products
In the realm of Data Products, where the stakes are high and the potential for innovation boundless, success hinges on the strength of the foundational building blocks. Imagine constructing a skyscraper – its stability and resilience lie in the integrity of its foundation. Similarly, the potency of Data Products is grounded in three essential building blocks: Data Quality and Reliability, User-Centric Design Principles, and Scalability and Performance Considerations.
Data Quality and Reliability
At the core of any impactful Data Product is the quality and reliability of the data it processes. Imagine building a recommendation engine with flawed or inaccurate data – the results would be far from insightful. We'll delve into the critical importance of maintaining clean, accurate, and up-to-date data. Real-world examples will illustrate the cascading effects of poor data quality on the functionality and effectiveness of Data Products. From inaccurate predictions to compromised user experiences, understanding the significance of pristine data is pivotal.
Imagine a weather app providing inaccurate forecasts due to flawed input data – the consequences could range from inconvenience to potential safety hazards. By exploring such scenarios, we'll highlight the paramount role of data quality in ensuring the reliability and credibility of Data Products.
User-Centric Design Principles
User experience is the heartbeat of Data Products. They're not just tools; they're companions in the user's digital journey. We'll unravel the art of crafting Data Products that resonate with users, enhancing their experience through every interaction. Drawing from design thinking principles, we'll explore how user-centric design goes beyond aesthetics, encompassing intuitive interfaces, personalized recommendations, and seamless interactions.
For example, in the evolution of smartphone keyboards – predictive text algorithms learn user preferences over time, making typing a personalized and efficient experience. Through such examples, we'll showcase how user-centric design transforms Data Products from mere utilities into indispensable components of users' digital lives.
Scalability and Performance Considerations
As the demand for Data Products grows, so does the need for scalability and optimal performance. Imagine a ride-sharing app that crashes during peak hours due to inadequate scalability. We'll dive into the technological challenges of handling massive datasets and ensuring optimal performance, especially in scenarios of increased user demand.
From distributed computing to cloud scalability, we'll explore the engineering feats required to build Data Products that can seamlessly evolve with the ever-expanding landscapes of data. Real-world examples will illustrate instances where the lack of scalability has hindered user experiences and organizational growth, emphasizing the importance of robust technological foundations.
In essence, these building blocks form the bedrock of successful data-driven innovations. Data quality, the design principles guiding user experiences, and the ability to scale and perform under increasing demands collectively define the potential and impact of Data Products. As we continue our exploration, these foundational elements will serve as our guiding pillars, unveiling the intricacies that set the stage for transformative data-driven solutions.
Data debt
Data Debt, in essence, refers to the compromises and shortcuts taken in the process of managing and handling data that result in future challenges. These compromises can take various forms, including suboptimal data modeling, inconsistent data quality, or even the neglect of necessary documentation.
Check out my article on the topic to learn how to harness Data Debt correctly.

Case Studies in Action
Netflix Recommendation Engine
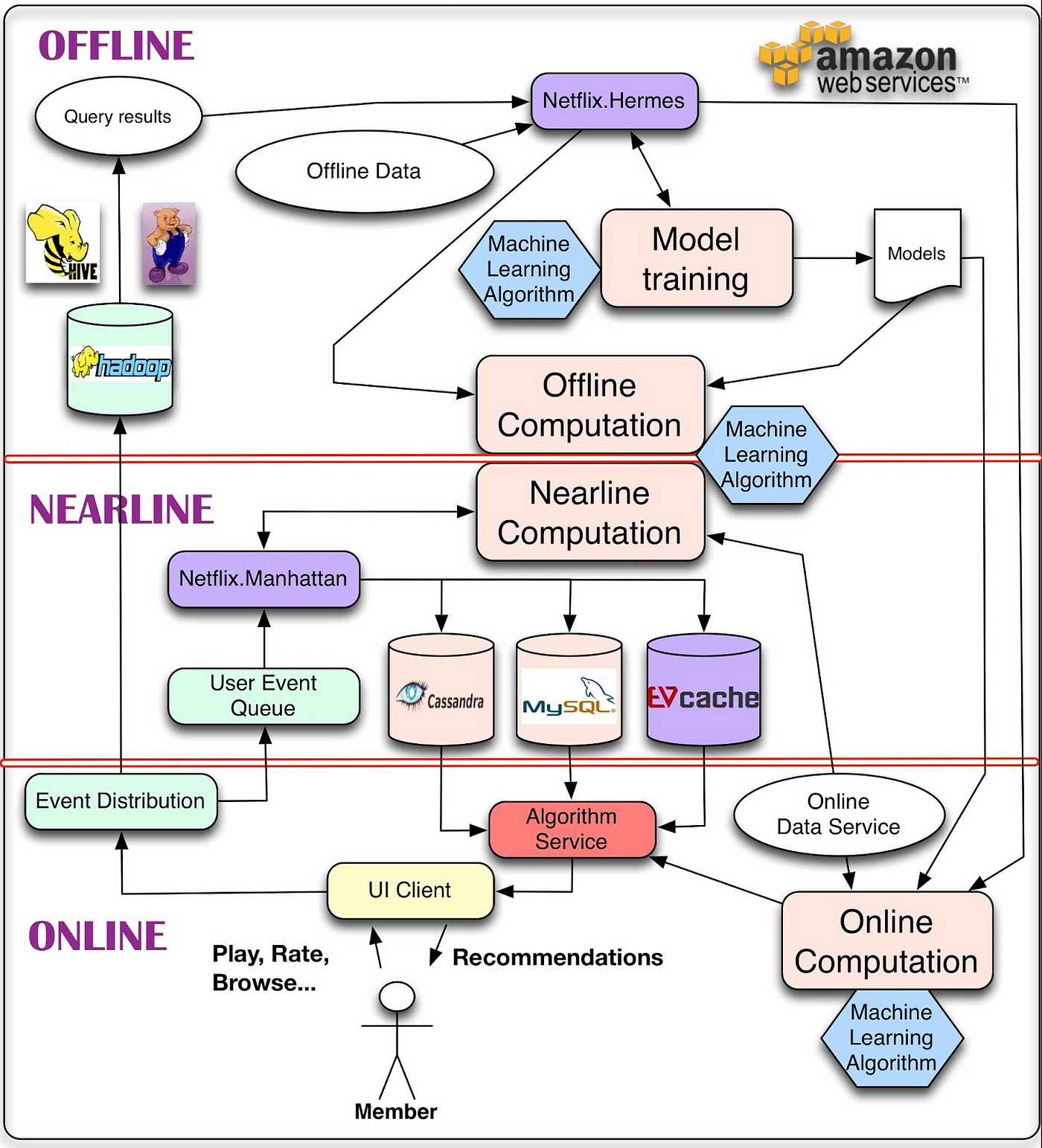
Let's zoom in on one of the most iconic examples of a Data Product in action – Netflix's recommendation engine. It's not just suggesting movies; it's predicting what you want to watch before you even know it. We'll unravel the magic behind the algorithms, exploring concepts like collaborative filtering and machine learning. By understanding how Netflix transforms user preferences into personalized content recommendations, we'll appreciate the sheer brilliance of Data Products in the entertainment industry.
Consider a weekend binge-watching session – each recommended title is a result of intricate algorithms analyzing your viewing history, comparing it to others with similar tastes, and predicting what you might enjoy next. It's not just about watching; it's about creating a continuous, tailored viewing experience, making every click a step toward a more personalized entertainment journey.
Amazon's Personalized Shopping Recommendations

Shift gears from movies to online shopping, and we encounter another Data Product maestro – Amazon's personalized shopping recommendations. Ever wondered how it knows what you need even before you do? We'll dissect the algorithms that power Amazon's recommendation engine, diving into the world of collaborative filtering and predictive analytics.
Picture this: you're browsing for a new gadget, and suddenly, Amazon suggests accessories and complementary items that seem almost psychic in their accuracy. This isn't a coincidence; it's the result of robust Data Products at work. By understanding user behavior, analyzing purchasing patterns, and predicting future needs, Amazon has transformed online shopping into a personalized and intuitive experience.
Tesla's Autopilot and Fleet Learning
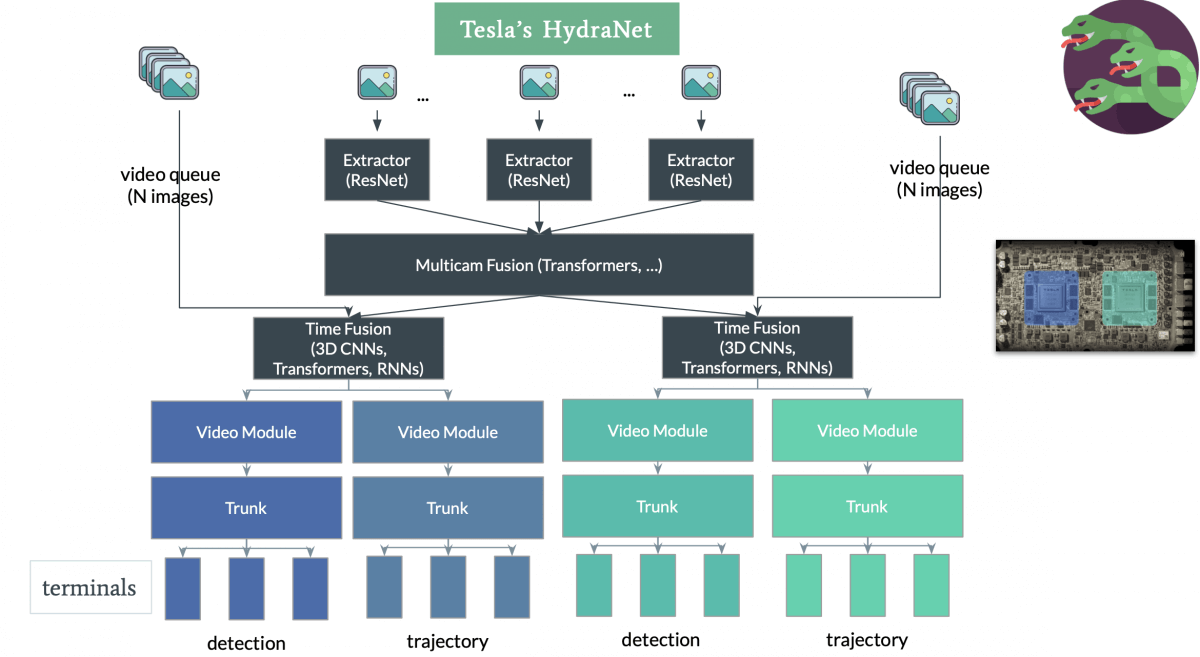
Now, let's hit the road with Tesla's Autopilot and Fleet Learning. Beyond being an electric car, Tesla's vehicles are rolling data hubs, constantly collecting information about road conditions, driver behavior, and more. We'll delve into the intricacies of how Tesla utilizes this data to improve its Autopilot feature, making every Tesla on the road a contributor to a collective intelligence.
Consider the autonomous capabilities of Tesla vehicles – each mile driven is a lesson learned, contributing to the evolution of the entire fleet. We'll explore how data from sensors, cameras, and real-world scenarios enable continuous improvement, turning each Tesla into not just a mode of transportation but a participant in the ongoing development of autonomous driving technology.
In these case studies, we witness Data Products in action, shaping user experiences and driving innovation in the entertainment, e-commerce, and automotive industries. Each example is a testament to the transformative power of data-driven insights, highlighting how Data Products aren't just tools but dynamic, evolving companions in our digital journeys. As we continue our exploration, these case studies serve as windows into the versatility and impact of Data Products across different domains.
Data Products vs. Traditional Software Products
Advantages and Disadvantages
In the ever-evolving landscape of technological innovation, the dichotomy between Data Products and their traditional counterparts is both stark and nuanced. Traditional products, rooted in providing immediate solutions, often serve a singular purpose at a specific point in time. Take a taxi service, for instance – hailed on the street to meet an immediate need for transportation.
On the flip side, Data Products extend beyond the immediacy of traditional services. They are dynamic, continuously evolving solutions that adapt to user behavior and preferences. Consider the difference between a traditional taxi service and a ride-sharing platform like Uber. While the former fulfills the immediate need for transportation, the latter adapts in real-time, optimizing routes based on traffic conditions and predicting demand. The advantage here lies in real-time adaptability, offering a personalized and efficient service that transcends the limitations of traditional models.
However, this adaptability comes with its own set of challenges. Data Products are inherently dependent on continuous data streams. The algorithms powering these products thrive on a constant influx of data to maintain relevance and provide accurate insights. This reliance on real-time data introduces complexities in managing and analyzing vast streams of information, a challenge less pronounced in traditional models.
Impact on User Experience
User experience stands at the forefront of the comparison between Data Products and traditional offerings. Traditional products provide tangible, often hands-on experiences. Consider the experience of shopping at a physical retail store – the ability to touch and feel products before making a purchase decision.
In contrast, Data Products redefine user interactions, offering a different dimension of experience. E-commerce platforms, for example, leverage data to provide personalized shopping recommendations. The algorithms analyze user behavior, understand preferences, and suggest products tailored to individual tastes. This not only enhances user satisfaction but also streamlines the shopping journey. However, as Data Products become more personalized, concerns about user privacy and data security come into play, requiring a delicate balance between customization and protecting user rights.
Future Trends and Predictions
As we peer into the future, the divergence between Data Products and traditional models becomes even more pronounced. Emerging technologies are poised to reshape the landscape, and Data Products will be at the forefront of this transformation.
A timely example is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in virtual assistants. While traditional products may respond to commands, Data Products infused with AI learn, predict, and adapt to user behavior. This evolution goes beyond mere functionality, offering anticipatory features that enhance user experiences.
The prediction for the next decade suggests a seamless integration of emerging technologies into Data Products, propelling them into uncharted territories. As AI becomes more sophisticated, virtual assistants may not only respond to queries but also proactively anticipate user needs. This trend signifies a paradigm shift in how users interact with products, creating a more intuitive and personalized digital experience.
In essence, the comparison between Data Products and traditional offerings highlights the evolving nature of the digital landscape. While traditional models excel in immediate solutions and hands-on experiences, Data Products redefine the rules of engagement. As we traverse the path to the future, the key lies in understanding the advantages and challenges of each and finding a harmonious coexistence where innovation meets user needs seamlessly.
Navigating Ethical Concerns
Privacy Issues in Data Products
In the era of data abundance, the ethical considerations surrounding privacy in Data Products are paramount. As organizations harness the power of data to fuel innovation, the delicate balance between extracting insights and respecting user privacy becomes a central theme.
Consider the data collected by fitness apps, which monitor and analyze users' health metrics. While this data is instrumental in providing personalized recommendations and insights, it simultaneously raises questions about user consent and the potential misuse of sensitive health information. This scenario underscores the ethical tightrope organizations walk when handling personal data.
Navigating privacy issues requires a commitment to transparent data practices. Organizations must prioritize user consent, clearly communicate how data will be used, and implement robust anonymization techniques to protect sensitive information. By examining real-world examples of both responsible and questionable data practices, we gain insights into the ethical dimensions that accompany the utilization of personal data in the development and deployment of Data Products.
Regulatory Compliance Challenges
The legal landscape governing data usage is dynamic and complex. Data Products must navigate a maze of regulations, from the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) to emerging global standards. The challenges organizations face in staying compliant with these regulations are manifold, requiring a proactive approach to understanding and adhering to legal frameworks.
Take a look at the challenges faced by social media platforms in maintaining compliance with privacy regulations. The tension between pushing technological boundaries for innovation and respecting the legal constraints of data protection laws is a delicate balance. We delve into case studies and practical insights to explore how organizations grapple with the evolving legal landscape, providing a roadmap for others in the data-driven space to navigate regulatory compliance challenges effectively.
Striking the Balance: Innovation vs. Privacy
In the age of constant innovation, finding the equilibrium between pushing technological boundaries and respecting privacy is a delicate dance. Organizations must not only prioritize user consent and data protection but also embrace responsible data practices that foster innovation without compromising user trust.
Consider the vision of a future where smart home devices anticipate user needs without compromising privacy. Achieving this balance requires not only technological prowess but also a commitment to ethical data handling. Through exploration and analysis, we uncover the complexities organizations face in their pursuit of cutting-edge Data Products. Striking this balance isn't just a regulatory requirement; it's a strategic imperative for building a trustworthy and sustainable data-driven ecosystem.
In essence, the exploration of ethical concerns in Data Products underscores the critical importance of responsible data practices. From privacy issues and regulatory challenges to the delicate balance between innovation and user trust, organizations must navigate this ethical tightrope to ensure that the transformative power of data is harnessed responsibly and ethically.
The Future of Data Products
The future is a realm of endless possibilities, especially in the dynamic landscape of Data. As we stand at the present and future crossroads, it's time to peer into the crystal ball and explore the exciting developments that await us.
Emerging Technologies Shaping the Landscape
The evolution of Data Products is intrinsically tied to the emergence of cutting-edge technologies. Advanced analytics is undergoing a metamorphosis, moving beyond mere predictions to prescriptive insights. Imagine a scenario where your data not only forecasts trends but also guides you on optimal actions to maximize outcomes. The integration of augmented reality into Data Products opens new frontiers, creating immersive and interactive experiences that redefine user engagement.
Consider a retail environment where augmented reality transforms the shopping experience. Visualize trying out furniture in your living room virtually before making a purchase decision. This is the future that emerging technologies promise for Data Products – a realm where insights are not just observed but experienced.
Potential Disruptions and Innovations
The tech landscape thrives on disruption, and the world of Data Products is no exception. Blockchain, once synonymous with cryptocurrencies, is making waves in data security. The decentralized and tamper-resistant nature of blockchain holds the potential to revolutionize how data is stored, ensuring unprecedented levels of security and trust.
Democratization of AI is another seismic shift on the horizon. As AI becomes more accessible, the power of advanced analytics will be in the hands of a broader audience. Imagine small businesses harnessing the capabilities of AI for personalized customer experiences or individuals leveraging AI for data-driven decision-making. This democratization not only levels the playing field but also sparks a wave of innovation across industries.
Predictions for the Next Decade
As we gaze into the future, what can we expect in the next decade of Data Products? Business models will undergo a profound transformation, driven by the increasing integration of data into decision-making processes. With AI being integrated into everything, the boundary between physical and digital realms will blur further, creating seamless, interconnected experiences.
Picture a scenario where your car not only navigates the roads but also interacts with smart city infrastructure, optimizing traffic flow based on real-time data. This integration is just a glimpse of the societal impacts that data-driven innovations will usher in.
In the next decade, Data Products will not be confined to the realm of business decisions. They will become integral to addressing societal challenges, from healthcare to environmental sustainability. Predictive analytics will play a pivotal role in healthcare, enabling early detection and personalized treatment plans. Environmental monitoring powered by data will contribute to more sustainable practices, ensuring a healthier planet for future generations.
Language Models (LLMs) and the Shaping of the Future
In the landscape of data-driven innovations, Language Models (LLMs) stand as a testament to the transformative power of artificial intelligence in shaping the future. LLMs, with their ability to comprehend and generate human-like text, have become pivotal in numerous applications, and their influence continues to grow.
Obviously, LLMs get their own section in every data-related article.
The Rise of LLMs
The emergence of sophisticated language models, powered by deep learning algorithms, marks a paradigm shift in how machines interact with human language. Models like GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) have demonstrated an unprecedented capacity to understand context, nuances, and even generate coherent and contextually relevant text. This transformative capability has far-reaching implications across various industries.
Applications Across Industries
The versatility of LLMs is evident in their applications across diverse sectors. In healthcare, LLMs assist in natural language processing, extracting insights from medical literature, and even generating summaries for complex research papers. In finance, these models aid in sentiment analysis, risk assessment, and customer interactions. Moreover, LLMs play a crucial role in the development of virtual assistants, language translation tools, and content-generation platforms.
Take a minute to think about the impact of a customer service chatbot powered by an advanced LLM. It can understand and respond to customer queries with a level of nuance and context awareness that was previously reserved for human interactions. This not only enhances user experiences but also augments the efficiency of customer service operations.
Ethical Considerations
However, the rise of LLMs is not without its ethical considerations. The sheer power and complexity of these models bring forth concerns about biases, misinformation, and the ethical use of AI in decision-making processes. As LLMs become more ingrained in daily interactions, addressing these ethical challenges becomes paramount to ensure responsible and equitable deployment.
Exploring and mitigating biases in language models, ensuring transparency in their decision-making processes, and implementing ethical guidelines for their development are crucial steps in navigating the ethical dimensions of LLMs. The responsible use of this technology is essential in fostering trust and ensuring that its benefits are realized without unintended consequences.
Shaping Communication and Creativity
Beyond their applications in specific industries, LLMs are shaping the very nature of communication and creativity. Content creation, once solely within the domain of human creators, is now being assisted and augmented by language models. From automated content summarization to creative writing prompts, LLMs are influencing the way information is conveyed and stories are told.
Imagine a future where content creators collaborate seamlessly with language models to enhance their creative processes. This collaborative approach, where human ingenuity is complemented by the computational power of LLMs, has the potential to redefine the boundaries of creativity and innovation.
Future Trajectory
As we peer into the future, the trajectory of LLMs seems boundless. Their evolution is likely to be marked by increased contextual understanding, enhanced creativity, and a deeper integration into various aspects of our daily lives. The ongoing research and development in natural language processing and machine learning promise to unlock new frontiers in the capabilities of LLMs.
Conclusion
Our journey through the world of Data Products has unveiled a tapestry woven with threads of innovation, ethics, and the future. Data, once a mere commodity, emerges as a transformative force, powering personalized experiences and shaping business strategies. As we navigate the delicate balance between innovation and privacy, we recognize the moral imperative of ethical data handling.
Looking to the future, we see promises of emerging technologies, potential disruptions, and societal impacts. The next decade holds the integration of advanced analytics, the democratization of AI, and interconnected experiences blurring physical and digital boundaries. Data isn't just a tool; it's empowerment – for industries, user experiences, and societal well-being.

Member discussion